Simple:Fgisqyf34wy= Ribosomes
Ribosomes are fundamental components of cellular machinery, intricately designed from ribonucleic acid and proteins, and consist of two distinct subunits that facilitate the translation of messenger RNA into polypeptides. Their pivotal role in protein synthesis underscores not only their importance in maintaining cellular function but also their emerging applications in biotechnology. As we explore the nuanced structure and multifaceted functions of ribosomes, one must consider how advancements in our understanding could reshape therapeutic strategies and the future of protein production. What implications might these developments hold for both science and medicine?
Structure of Ribosomes
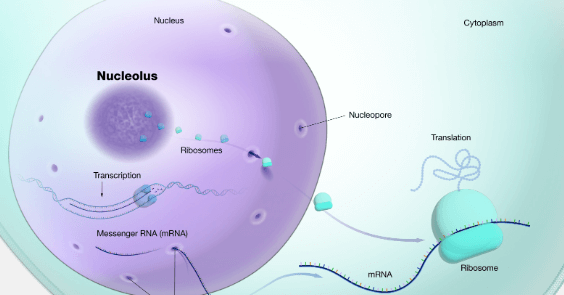
Ribosomes, complex ribonucleoprotein structures, are composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins, organized into two subunits that facilitate the synthesis of polypeptides during translation.
The large subunit typically contains three rRNA molecules, while the small subunit comprises one rRNA molecule.
This intricate architecture is crucial for the fidelity and efficiency of protein synthesis, underscoring the essential role of ribosomes in cellular function.
See also: Simple:D32lkumiol0= Tattoo
Function of Ribosomes
The primary function of ribosomes is to catalyze the translation of messenger RNA (mRNA) into polypeptide chains, thereby playing a pivotal role in protein synthesis within the cell.
Ribosome synthesis occurs in the nucleolus, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins assemble.
This intricate process ensures that protein translation is efficient, allowing cells to produce the necessary proteins for various biological functions and maintaining cellular integrity.
Ribosomes in Biotechnology
In biotechnology, ribosomes are harnessed for their ability to facilitate recombinant protein production, enabling the synthesis of therapeutic proteins and enzymes through engineered mRNA templates.
Ribosome engineering, a pivotal aspect of synthetic biology, allows for the customization of ribosomal activity, optimizing translation efficiency and specificity.
This innovation is instrumental in developing biopharmaceuticals and advancing our understanding of cellular mechanisms.
Conclusion
In the grand symphony of cellular function, ribosomes serve as masterful conductors, orchestrating the translation of genetic blueprints into the harmonious melodies of proteins.
Their intricate structure and dynamic functionality not only underpin the vitality of life but also illuminate pathways for biotechnological advancements.
As these cellular artisans continue to refine the art of protein synthesis, they pave the way for innovative therapeutic applications, embodying the relentless pursuit of knowledge and the artistry of biological engineering.




